Building AI Agents with Model Context Protocol (MCP) - A Complete Guide
Learn how to transform Claude AI into a powerful AI agent using Model Context Protocol (MCP). Step-by-step guide with GitHub integration, Docker setup, and practical examples.

Introduction
Generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini have revolutionized how we interact with AI. But what if your AI could do more than just chat? What if it could actually perform tasks, manage repositories, and automate workflows?
In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn how to transform Claude AI from a simple chatbot into a powerful AI agent using Model Context Protocol (MCP). We'll walk through setting up MCP with Docker, integrating GitHub, and creating your first AI agent that can interact with real-world systems.
Table of Contents
- What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
- Setting up the environment
- Configuring the MCP Server
- Practical Example
- Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Why Use It?
MCP is in its early stages and many features are still experimental. There are also dependency chains that can introduce supply chain attack risks. Use with caution. Please see the link below for more information.
LLMs are great at understanding prompts and generating responses. However, they struggle with understanding APIs and how to use them effectively.
That's where MCP comes into play. MCP is a protocol that allows LLMs to understand and use APIs by providing a structured way to define the model's context. This includes information about the APIs, their parameters, and how to use them.
We're not digging too deep here, but this YouTube video from NetworkChuck explains it well:
Setting up the environment
In this lab, we are going to work on a GitHub Repository with LLM and MCP support. Our LLM of choice is Claude Sonnet 4.5. We are integrating GitHub's Official MCP in Claude Desktop App.
Prerequisites
- Docker Desktop 4.35+ (with MCP Toolkit support)
- A GitHub Account with a repository to test
- GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) with repo permissions
- Claude Pro Account (for Claude Desktop app access)
- Operating System: macOS, Windows, or Linux
Configuring the MCP Server in Docker Desktop
Later versions of Docker Desktop come with an experimental feature called MCP Toolkit. This allows us to run containerized MCP servers locally. This is a great way to keep things simple and avoid installing NodeJS and other dependencies on our local machine.
-
Verify it's enabled by going to Settings > Experimental Features and checking the box for Enable MCP Toolkit. After enabling it, you will need to restart Docker Desktop.

-
Open MCP Toolkit. Go to "Catalog" and search for "GitHub Official". Open it and click "Add MCP Server".

-
Add your GitHub PAT in the configuration.
-
Go to "Clients" and select "Claude Desktop". Click "Connect". This add some JSON for you in Claude Desktop's configuration.

-
Open Claude Desktop. The MCP server should be active now.

-
Verify in Docker Desktop as well. The image should be there.

Practical Example: Using Claude AI Agent with GitHub
Now that we have everything set up, let's try it out. Open Claude Desktop and create a new chat. Make sure the MCP server is active.
First of all, a LLM needs a well crafted prompt in order to do something useful. Here is my prompt for this example:
# Verify access to repo
You are an AI based DevOps expert with extensive knowledge in IaC like Terraform and how to manage Github repositories as well as documentation best practises.
## Repo info
- GitHub account: jihillestad
- Repo: tflab-linux
- Repo type: Private
_ Project type: Terraform IaC for creating a simple landing zone and a Linux VM
## Request
- Verify that you can access the repo
- Quality check the root README.md
Create a prompt like this in Claude Desktop and send it. The LLM will now use the MCP server to access the GitHub API and perform the tasks. As you can see in the images below, there are some guardrails in place to make sure you approve every action before it is performed.

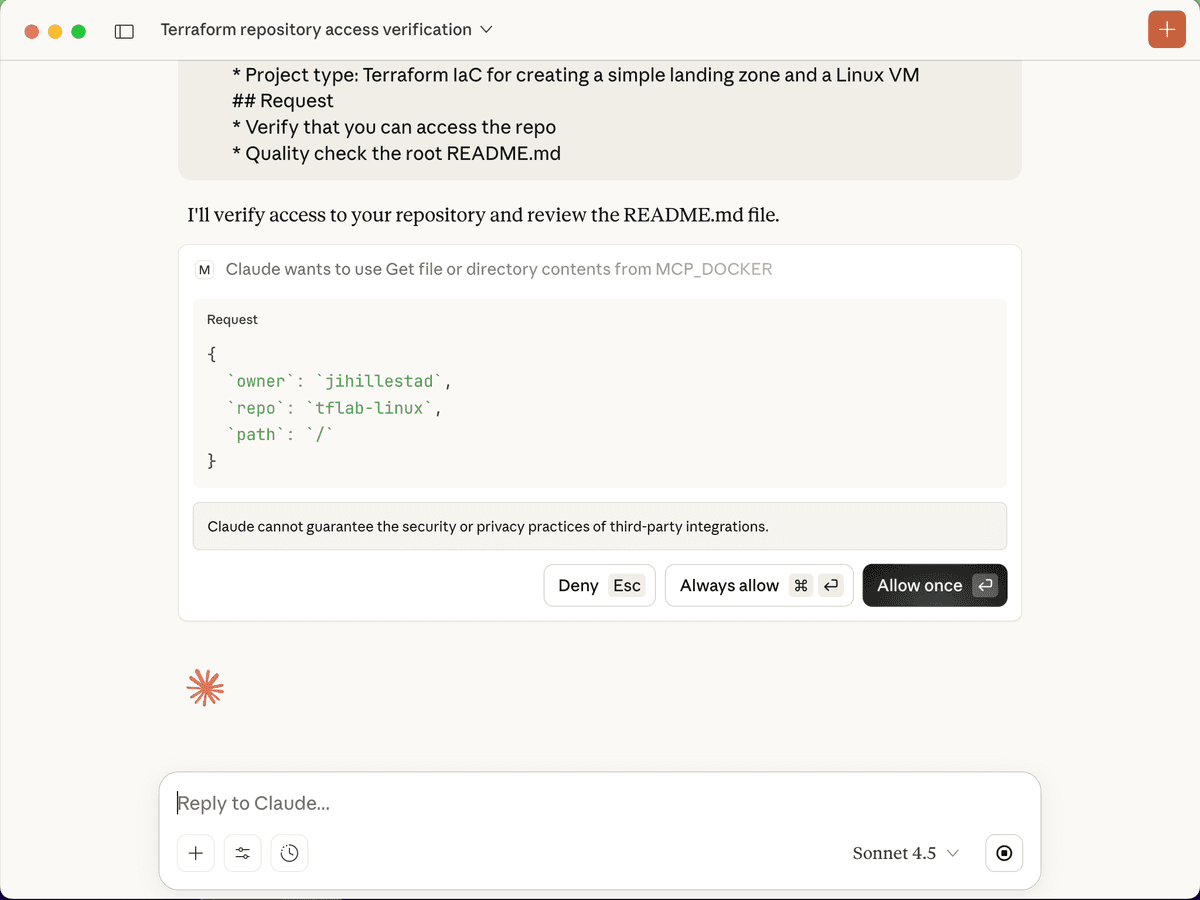
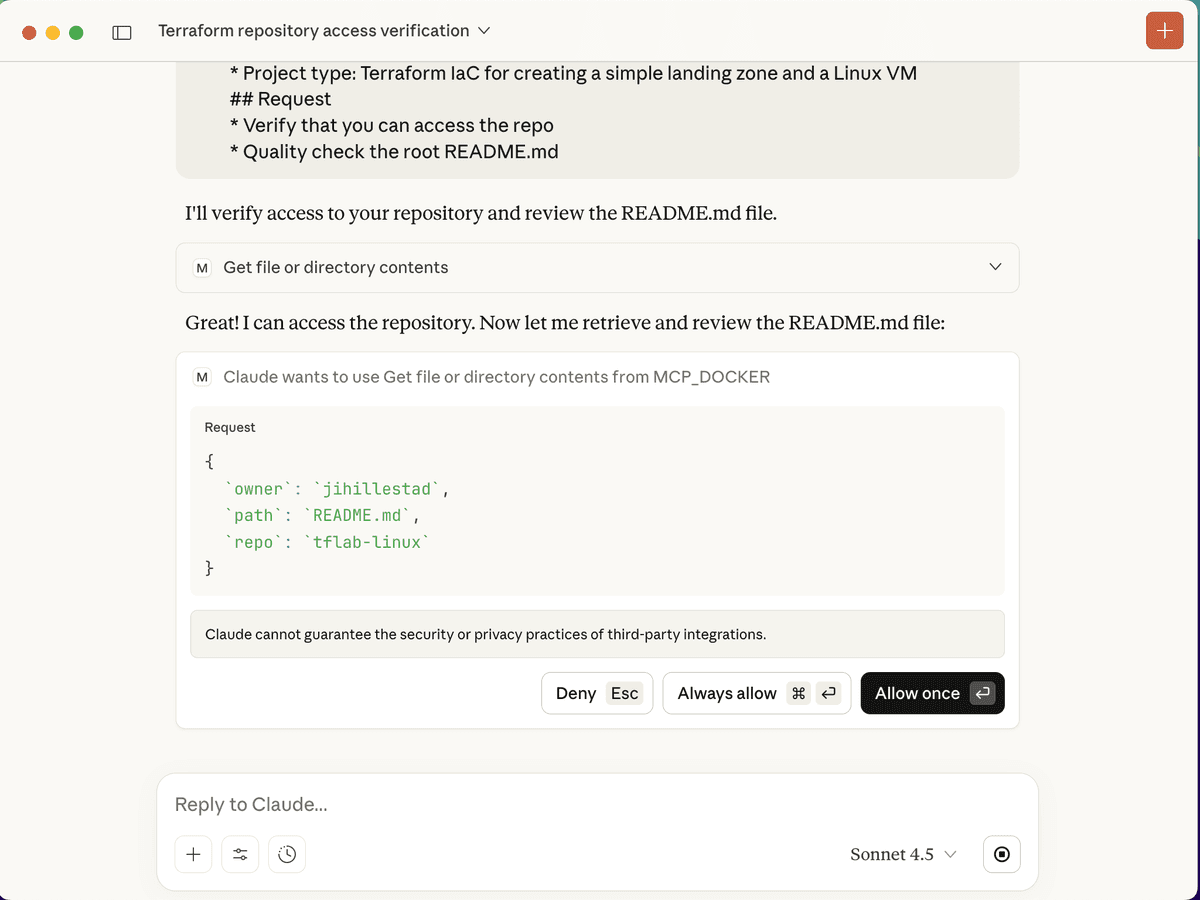

Troubleshooting Common Issues
MCP Server Not Connecting
- Ensure Docker Desktop is running
- Verify the GitHub PAT has correct permissions (repo access required)
- Restart Claude Desktop after configuration changes
- Check that MCP Toolkit is enabled in Docker Desktop experimental features
404 Errors When Accessing Repository
- Check if the PAT has access to private repositories
- Verify the repository name and owner are correct
- Ensure the MCP server is active in Claude Desktop (look for the server icon)
- Confirm your GitHub token hasn't expired
MCP Server Container Not Starting
- Check Docker Desktop logs for errors
- Verify sufficient system resources are available
- Try removing and re-adding the MCP server in MCP Toolkit
- Ensure you're using Docker Desktop 4.35 or later
Key Takeaways
- 🤖 MCP transforms LLMs into actionable AI agents
- 🐳 Docker Desktop simplifies MCP server management
- 🔗 GitHub integration enables repository automation
- ✅ Built-in guardrails ensure safe AI operations
- 🚀 Extensible architecture supports multiple MCP servers
Ready to Build Your Own AI Agent?
Now that you've seen how MCP works, why not try it yourself? Start with a simple repository and expand from there. The possibilities are endless - from automated code reviews to infrastructure management and documentation updates.
Have questions or built something cool with MCP? I'd love to hear about your experiences!
Conclusion
As you can see, it's quite easy to give a LLM agent-like capabilities using MCP. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities for automating tasks and making AI more productive. These capabilities can be expanded even further by adding more MCP servers for other APIs and services.
We are not doing fully autonomous Agentic AI here yet, but we are getting there. The future is bright!